Learn How To Diagnose Fallen Arches
Overview
It is rare to find someone who walks with both feet in perfect alignment. A foot that is flat or has a very high arch does not necessarily require treatment unless there is pain. Often we walk on the inside or outsides of our feet, or with our toes or heels rotated inward or outward more than they should be. These atypical walking patterns can cause many problems not just with the feet but also for the whole body as the alignment of the feet sets the foundation for the whole body?s alignment. One of the most common effects of improper alignment is known as flatfoot, or pes planus.
Causes
There are a number of different causes that can lead to flat feet or fallen arches. These include, birth defects, while technically not a defect as such, flat feet can be a normal finding in patients from birth. However, a condition called tarsal coalition may occur where some of the bones in the foot are fused together resulting in a flatfoot. Inflammation or damage of the posterior tibial tendon. This tendon forms the end of a muscle that connects the lower leg to the foot, winding around the ankle and attaching to the inner aspect where the arch is normally present. The main role of the posterior tibial tendon is to invert the foot and maintain the arch height throughout the gait cycle. Torn muscles of the leg and foot can cause flat feet. Problems with the nerve supply to the muscles can result in reduction in tone and fallen arches. Fracture dislocation of the bones in the foot. Severe arthritis. While these are the common causes that can result in fallen arches and flat feet, it is important to recognise that there are certain risk factors that can also lead to this condition. These include advancing age, diabetes mellitus, high blood pressure, obesity and pregnancy.
Symptoms
Flat feet can cause a myriad of symptoms, from experiencing pain in the foot, heels, arch, calves, the shin, the knee, the hip and into the lower back due to overworking of the hip flexors or they may find it hard to stand on tip toes.
Diagnosis
It is important for people with foot pain to know if they have flat feet. The following tests can help you determine your arch type. When you get out of a swimming pool, look at your footprint on the concrete. The front of the foot will be joined to the heel by a strip. If your foot is flat, then the strip is the same width as the front of the foot, creating a footprint that looks like a stretched out pancake. With a normal arch, the strip is about half the width of the front of the foot. If you have a high arch, only a thin strip connects the front of the foot with the heel. Put your shoes on a flat table and view them at eye level from behind. See if the sole is worn evenly. A flat foot will cause more wear on the inside of the sole, especially in the heel area. The shoe will easily rock side to side. A flat foot will also cause the upper part of the shoe to lean inward over the sole. Both shoes should wear about the same way. If you have pain in one foot, you should make sure you don't have a fallen arch on that side. There are two good tests you can perform at home to detect this problem. Place your fingertips on a wall that you are directly facing and stand on your tiptoes on one foot. If you can't do it, a fallen arch may be the culprit. Stand with your feet parallel. Have someone stand in back of you and look at your feet from behind. You can also do it yourself if you stand with your back to a mirror. Normally, only the pinky toe is visible from behind. If one foot is flatter than the other, the 4th and sometimes the 3rd toe on that foot can also be seen.
pes cavus
Non Surgical Treatment
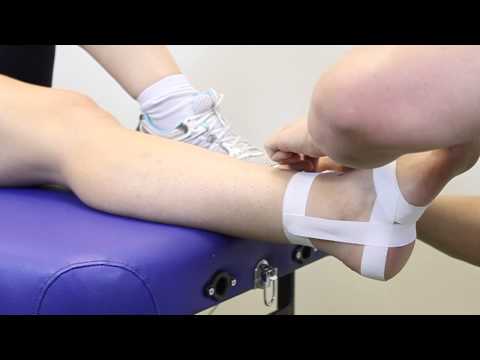
Foot orthotic devices can stabilize some of the causes of flat feet, optimize muscle function and reduce the occurrence of painful symptoms. Generally, a custom-made semi-rigid functional posted orthotic is effective for flat feet. These devices are prescribed based on a thorough biomechanical examination by a qualified chiropodist/podiatrist. Over-the-counter arch supports may be helpful for mild cases, but often prove ineffective to relieve symptoms associated with flatfoot. Wear shoes with a good fit in the arch. Keep active and fit to strengthen leg and foot musculature. Control body weight to decrease load on the feet. Avoid prolonged periods weight bearing with bare feet. Taping to support strained ligaments and joints. Physical therapy modalities such as ultrasound. Referral for surgical correction a severe symptomatic flatfoot.
Surgical Treatment

Common indications for surgery are cerebral palsy with an equinovalgus foot, to prevent progression and breakdown of the midfoot. Rigid and painful Pes Planus. To prevent progression, eg with a Charcot joint. Tibialis posterior dysfunction, where non-surgical treatment is unsuccessful. Possible surgical procedures include Achilles tendon lengthening. Calcaneal osteotomy, to re-align the hindfoot. Reconstruction of the tibialis posterior tendon. For severe midfoot collapse of the arch, triple arthrodesis may be indicated.
Prevention
Orthotic inserts, either prescribed or bought over the counter, can help keep the arches fixed into position, but always wear them as although they support, they don?t strengthen, which is why some experts reccomend avoiding them. Gait analysis at a run specialist can help to diagnose overpronation and flat feet. Most brands produce shoes that will give support and help to limit the negative effects of a poor gait on the rest of the body. Barefoot exercises, such as standing on a towel and making fists with the toes, can help to strengthen the arches. Start easy and build up the reps to avoid cramping. Short barefoot running sessions can help take pressure off the arches by using the natural elasticity of the foot?s tendons to take impact and build strength to help prevent flat feet. These should be done on grass for only a few minutes at a time.
After Care
Patients may go home the day of surgery or they may require an overnight hospital stay. The leg will be placed in a splint or cast and should be kept elevated for the first two weeks. At that point, sutures are removed. A new cast or a removable boot is then placed. It is important that patients do not put any weight on the corrected foot for six to eight weeks following the operation. Patients may begin bearing weight at eight weeks and usually progress to full weightbearing by 10 to 12 weeks. For some patients, weightbearing requires additional time. After 12 weeks, patients commonly can transition to wearing a shoe. Inserts and ankle braces are often used. Physical therapy may be recommended. There are complications that relate to surgery in general. These include the risks associated with anesthesia, infection, damage to nerves and blood vessels, and bleeding or blood clots. Complications following flatfoot surgery may include wound breakdown or nonunion (incomplete healing of the bones). These complications often can be prevented with proper wound care and rehabilitation. Occasionally, patients may notice some discomfort due to prominent hardware. Removal of hardware can be done at a later time if this is an issue. The overall complication rates for flatfoot surgery are low.

It is rare to find someone who walks with both feet in perfect alignment. A foot that is flat or has a very high arch does not necessarily require treatment unless there is pain. Often we walk on the inside or outsides of our feet, or with our toes or heels rotated inward or outward more than they should be. These atypical walking patterns can cause many problems not just with the feet but also for the whole body as the alignment of the feet sets the foundation for the whole body?s alignment. One of the most common effects of improper alignment is known as flatfoot, or pes planus.
Causes
There are a number of different causes that can lead to flat feet or fallen arches. These include, birth defects, while technically not a defect as such, flat feet can be a normal finding in patients from birth. However, a condition called tarsal coalition may occur where some of the bones in the foot are fused together resulting in a flatfoot. Inflammation or damage of the posterior tibial tendon. This tendon forms the end of a muscle that connects the lower leg to the foot, winding around the ankle and attaching to the inner aspect where the arch is normally present. The main role of the posterior tibial tendon is to invert the foot and maintain the arch height throughout the gait cycle. Torn muscles of the leg and foot can cause flat feet. Problems with the nerve supply to the muscles can result in reduction in tone and fallen arches. Fracture dislocation of the bones in the foot. Severe arthritis. While these are the common causes that can result in fallen arches and flat feet, it is important to recognise that there are certain risk factors that can also lead to this condition. These include advancing age, diabetes mellitus, high blood pressure, obesity and pregnancy.
Symptoms
Flat feet can cause a myriad of symptoms, from experiencing pain in the foot, heels, arch, calves, the shin, the knee, the hip and into the lower back due to overworking of the hip flexors or they may find it hard to stand on tip toes.
Diagnosis
It is important for people with foot pain to know if they have flat feet. The following tests can help you determine your arch type. When you get out of a swimming pool, look at your footprint on the concrete. The front of the foot will be joined to the heel by a strip. If your foot is flat, then the strip is the same width as the front of the foot, creating a footprint that looks like a stretched out pancake. With a normal arch, the strip is about half the width of the front of the foot. If you have a high arch, only a thin strip connects the front of the foot with the heel. Put your shoes on a flat table and view them at eye level from behind. See if the sole is worn evenly. A flat foot will cause more wear on the inside of the sole, especially in the heel area. The shoe will easily rock side to side. A flat foot will also cause the upper part of the shoe to lean inward over the sole. Both shoes should wear about the same way. If you have pain in one foot, you should make sure you don't have a fallen arch on that side. There are two good tests you can perform at home to detect this problem. Place your fingertips on a wall that you are directly facing and stand on your tiptoes on one foot. If you can't do it, a fallen arch may be the culprit. Stand with your feet parallel. Have someone stand in back of you and look at your feet from behind. You can also do it yourself if you stand with your back to a mirror. Normally, only the pinky toe is visible from behind. If one foot is flatter than the other, the 4th and sometimes the 3rd toe on that foot can also be seen.
pes cavus
Non Surgical Treatment
Foot orthotic devices can stabilize some of the causes of flat feet, optimize muscle function and reduce the occurrence of painful symptoms. Generally, a custom-made semi-rigid functional posted orthotic is effective for flat feet. These devices are prescribed based on a thorough biomechanical examination by a qualified chiropodist/podiatrist. Over-the-counter arch supports may be helpful for mild cases, but often prove ineffective to relieve symptoms associated with flatfoot. Wear shoes with a good fit in the arch. Keep active and fit to strengthen leg and foot musculature. Control body weight to decrease load on the feet. Avoid prolonged periods weight bearing with bare feet. Taping to support strained ligaments and joints. Physical therapy modalities such as ultrasound. Referral for surgical correction a severe symptomatic flatfoot.
Surgical Treatment

Common indications for surgery are cerebral palsy with an equinovalgus foot, to prevent progression and breakdown of the midfoot. Rigid and painful Pes Planus. To prevent progression, eg with a Charcot joint. Tibialis posterior dysfunction, where non-surgical treatment is unsuccessful. Possible surgical procedures include Achilles tendon lengthening. Calcaneal osteotomy, to re-align the hindfoot. Reconstruction of the tibialis posterior tendon. For severe midfoot collapse of the arch, triple arthrodesis may be indicated.
Prevention
Orthotic inserts, either prescribed or bought over the counter, can help keep the arches fixed into position, but always wear them as although they support, they don?t strengthen, which is why some experts reccomend avoiding them. Gait analysis at a run specialist can help to diagnose overpronation and flat feet. Most brands produce shoes that will give support and help to limit the negative effects of a poor gait on the rest of the body. Barefoot exercises, such as standing on a towel and making fists with the toes, can help to strengthen the arches. Start easy and build up the reps to avoid cramping. Short barefoot running sessions can help take pressure off the arches by using the natural elasticity of the foot?s tendons to take impact and build strength to help prevent flat feet. These should be done on grass for only a few minutes at a time.
After Care
Patients may go home the day of surgery or they may require an overnight hospital stay. The leg will be placed in a splint or cast and should be kept elevated for the first two weeks. At that point, sutures are removed. A new cast or a removable boot is then placed. It is important that patients do not put any weight on the corrected foot for six to eight weeks following the operation. Patients may begin bearing weight at eight weeks and usually progress to full weightbearing by 10 to 12 weeks. For some patients, weightbearing requires additional time. After 12 weeks, patients commonly can transition to wearing a shoe. Inserts and ankle braces are often used. Physical therapy may be recommended. There are complications that relate to surgery in general. These include the risks associated with anesthesia, infection, damage to nerves and blood vessels, and bleeding or blood clots. Complications following flatfoot surgery may include wound breakdown or nonunion (incomplete healing of the bones). These complications often can be prevented with proper wound care and rehabilitation. Occasionally, patients may notice some discomfort due to prominent hardware. Removal of hardware can be done at a later time if this is an issue. The overall complication rates for flatfoot surgery are low.